Note(15-445/645 — INTRO TO DATABASE SYSTEMS)
Query Execution
Processing Models
- Iterator Model also known as Valcona Model or Pipeline. this model iterate over every tuple
- Materialization Model
- Vectorization Model: this model iterate over every batch
Access Methods
- Seq Scan
- Index Scan
Expression Evaluation
The DBMS represents WHERE clause as an expression tree.
Query Planning & Optimization
Logical Query Optimization
- Split Conjunctive Predicates
- Predicate Pushdown
- Replace Cartesian Products with Joins
- Projection Pushdown
Physical Query Optimization
Histogram
Count-Min Sketch: a probabilistic data structure that serves as a frequency table of events in a stream of data.
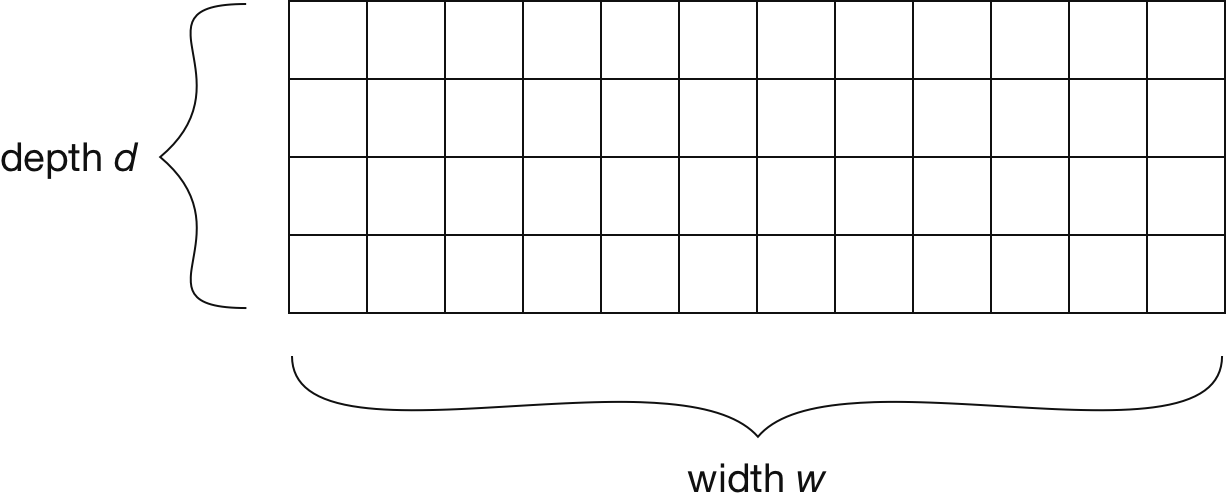
- Initialization: $\forall i \in {1, \dots, d}, j \in {1, \dots, w}, : \operatorname{count}[i, j] = 0$
- Increment count (of element $a$): $\forall i \in {1, \dots, d}: \operatorname{count}[i, h_i(a)] \mathrel{+}= 1$
- Retrieve count (of element $a$): $min_{i=1}^d \operatorname{count}[i, h_i(a)]$
HyperLogLog: an algorithm for the count-distinct problem, approximating the number of distinct elements in a multiset.
Sampling
- Reservoir Sampling
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18int[] reservoir = new int[m];
// init
for (int i = 0; i < reservoir.length; i++)
{
reservoir[i] = dataStream[i];
}
for (int i = m; i < dataStream.length; i++)
{
// 随机获得一个[0, i]内的随机整数
int d = rand.nextInt(i + 1);
// 如果随机整数落在[0, m-1]范围内,则替换蓄水池中的元素
if (d < m)
{
reservoir[d] = dataStream[i];
}
}Concurrency Control
Pessimistic Lock
Optimistic Lock
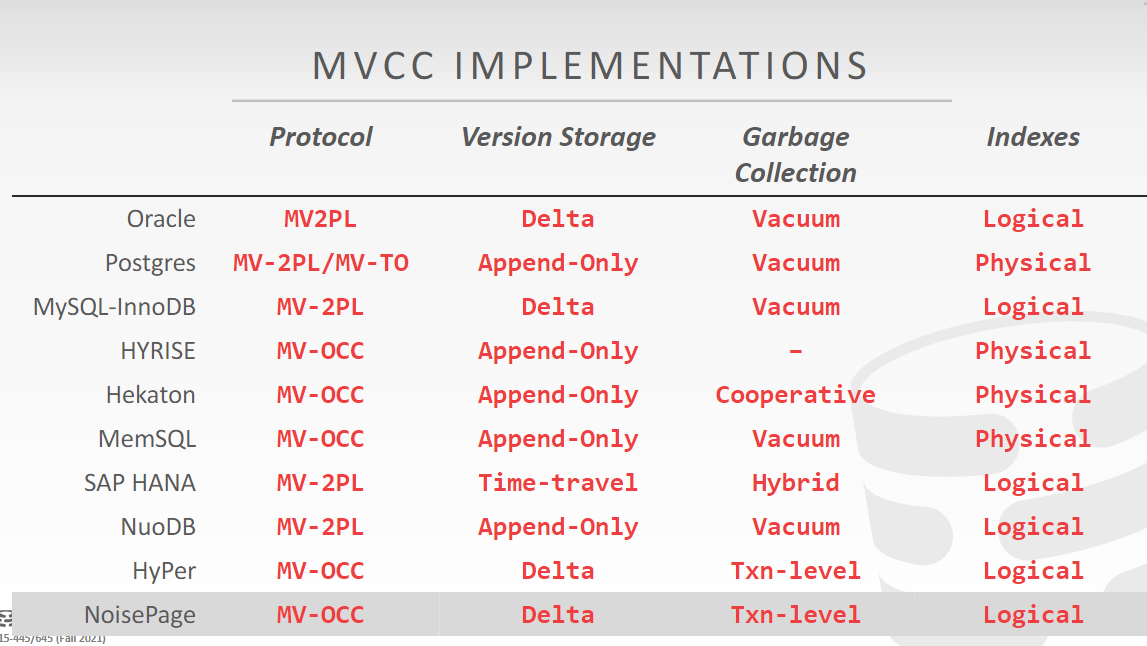
MVCC
MVCC can work with Optimistic Lock and Pessimistic Lock
Distribute Database
Crash Recovery
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!